DispatcherServlet初始化
说起springmvc我们自然会第一个想到,配置一个springmvc的web项目肯定是要先在web.xml中配置一个叫dispatcherServlet的servlet,servlet此处不做过多讨论,只是我们知道,servlet在web项目启动时会先调用他的init方法,我们顺着这个思路往下看,spring的这个dispatcherservlet他就是一个servlet。以下是他在spring中的uml图。他继承自FrameworkServlet,FrameworkServlet继承自HttpServletBean,再向上便是继承自HttpServlet,那他作为一个servlet自然会在项目启动时调用init方法,我们找到他的init() 方法。看一下他是如何一步一步初始化spring的。
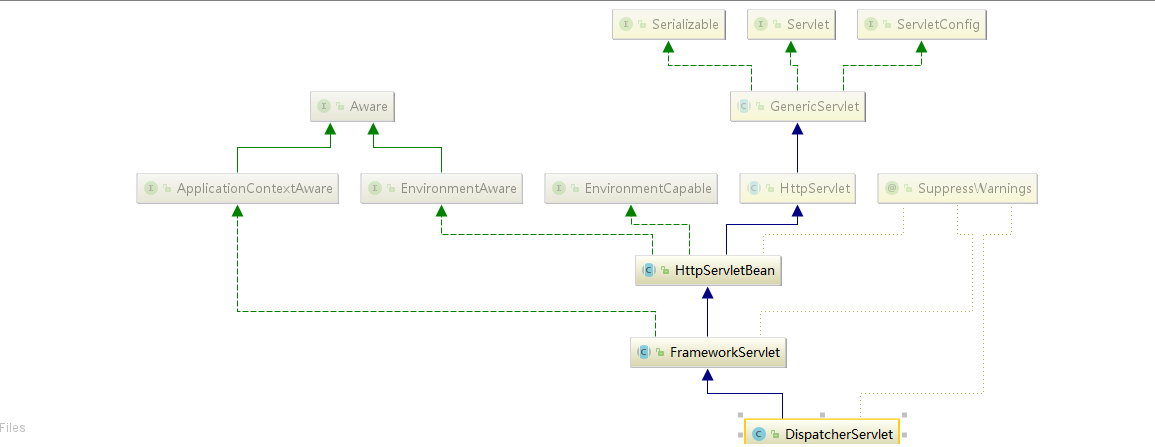
init方法在HttpServletBean中我们,首先他在初始化是先加载web.xml中 dispatcherservlet所在servlet对应的所有的标签的参数,整个spring初始化的init中initServletBean()最为关键。
public final void init() throws ServletException {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Initializing servlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
// Set bean properties from init parameters.
PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
try {
//创建一个bean包装类BeanWrapperImpl
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
//用当前上下文创建ResourceLoader资源加载器
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext());
//bw中注册一个用StandardServletEnvironment 创建的ResourceEditor
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment()));
//初始化bw用用户自己实现
initBeanWrapper(bw);
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) {
logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + getServletName() + "'", ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
// Let subclasses do whatever initialization they like.
initServletBean();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Servlet '" + getServletName() + "' configured successfully");
}
}
private static class ServletConfigPropertyValues extends MutablePropertyValues {
public ServletConfigPropertyValues(ServletConfig config, Set<String> requiredProperties)
throws ServletException {
Set<String> missingProps = (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(requiredProperties) ?
new HashSet<>(requiredProperties) : null);
//从servlet所对应的servletconfig中获取所有的<init-param>标签的内容 并将其包装成PropertyValue添加到List<PropertyValue> propertyValueList中
Enumeration<String> paramNames = config.getInitParameterNames();
while (paramNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String property = paramNames.nextElement();
Object value = config.getInitParameter(property);
addPropertyValue(new PropertyValue(property, value));
if (missingProps != null) {
missingProps.remove(property);
}
}
// Fail if we are still missing properties.
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(missingProps)) {
throw new ServletException(
"Initialization from ServletConfig for servlet '" + config.getServletName() +
"' failed; the following required properties were missing: " +
StringUtils.collectionToDelimitedString(missingProps, ", "));
}
}
}
此处关键在于初始化webApplicationContext 以下我们看下初始化的流程。
@Override
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "': initialization started");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
initFrameworkServlet();
}
catch (ServletException | RuntimeException ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "': initialization completed in " +
elapsedTime + " ms");
}
}
//////////////////////////////////////////
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
//从servlet上下文中查找是否有叫做org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext.ROOT的根上下文
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> set
// the root application context (if any; may be null) as the parent
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance was injected at construction time -> see if one
// has been registered in the servlet context. If one exists, it is assumed
// that the parent context (if any) has already been set and that the
// user has performed any initialization such as setting the context id
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance is defined for this servlet -> create a local one
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
// Either the context is not a ConfigurableApplicationContext with refresh
// support or the context injected at construction time had already been
// refreshed -> trigger initial onRefresh manually here.
synchronized (this.onRefreshMonitor) {
onRefresh(wac);
}
}
if (this.publishContext) {
// Publish the context as a servlet context attribute.
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Published WebApplicationContext of servlet '" + getServletName() +
"' as ServletContext attribute with name [" + attrName + "]");
}
}
return wac;
}
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(@Nullable ApplicationContext parent) {
//DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS XmlWebApplicationContext.class
Class<?> contextClass = getContextClass();
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Servlet with name '" + getServletName() +
"' will try to create custom WebApplicationContext context of class '" +
contextClass.getName() + "'" + ", using parent context [" + parent + "]");
}
//判断是不是他的继承类或实现类
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Fatal initialization error in servlet with name '" + getServletName() +
"': custom WebApplicationContext class [" + contextClass.getName() +
"] is not of type ConfigurableWebApplicationContext");
}
//反射实例化XmlWebApplicationContext
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac =
(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
//StandardServletEnvironment
wac.setEnvironment(getEnvironment());
//父上下文
wac.setParent(parent);
String configLocation = getContextConfigLocation();
if (configLocation != null) {
wac.setConfigLocation(configLocation);
}
// 初始化关键方法
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(wac);
return wac;
}
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac) {
if (ObjectUtils.identityToString(wac).equals(wac.getId())) {
// The application context id is still set to its original default value
// -> assign a more useful id based on available information
if (this.contextId != null) {
wac.setId(this.contextId);
}
else {
// Generate default id...
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX +
ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(getServletContext().getContextPath()) + '/' + getServletName());
}
}
wac.setServletContext(getServletContext());
wac.setServletConfig(getServletConfig());
wac.setNamespace(getNamespace());
//添加监听器 参考事件监听设计模式
wac.addApplicationListener(new SourceFilteringListener(wac, new ContextRefreshListener()));
// The wac environment's #initPropertySources will be called in any case when the context
// is refreshed; do it eagerly here to ensure servlet property sources are in place for
// use in any post-processing or initialization that occurs below prior to #refresh
ConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment();
//XmlWebApplicationContext 的环境 空的话默认创建一个 StandardEnvironment 环境
//StandardEnvironment 实现是ConfigurableEnvironment接口
//eg:StandardServletEnvironment 替换 PropertySource为ServletPropertySource
if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {
((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(getServletContext(), getServletConfig());
}
postProcessWebApplicationContext(wac);
//获取当前servlet上下文 的init-param 的globalInitializerClasses
//初始化 添加 ApplicationContextInitializer
//遍历调用initialize()初始化方法
applyInitializers(wac);
//* 刷新上下文 调用abstractapplicationcontext中的refresh
wac.refresh();
}